-
OpenAI has launched Codex, a powerful AI coding agent inside ChatGPT that can write, test, and commit real code using codex-1, a model fine-tuned for software development. Meanwhile, China’s Manus AI introduced a next-gen image generator that plans, designs, and executes complex visual tasks using a multi-agent system. At the same time, Anthropic is preparing a major upgrade to Claude with true agentic behavior, and Google is transforming Search with Gemini-powered AI Mode for smarter, conversational results.
https://youtu.be/wOfHX-efjX0?si=hEO3R2-uessVNQU-OpenAI has launched Codex, a powerful AI coding agent inside ChatGPT that can write, test, and commit real code using codex-1, a model fine-tuned for software development. Meanwhile, China’s Manus AI introduced a next-gen image generator that plans, designs, and executes complex visual tasks using a multi-agent system. At the same time, Anthropic is preparing a major upgrade to Claude with true agentic behavior, and Google is transforming Search with Gemini-powered AI Mode for smarter, conversational results. https://youtu.be/wOfHX-efjX0?si=hEO3R2-uessVNQU- 0 Comments ·0 Shares ·2K Views ·0 Reviews
0 Comments ·0 Shares ·2K Views ·0 Reviews -
We’re officially releasing the quantized models of Qwen3 today!
Now you can deploy Qwen3 via Ollama, LM Studio, SGLang, and vLLM — choose from multiple formats including GGUF, AWQ, and GPTQ for easy local deployment.
Find all models in the Qwen3 collection on Hugging Face and ModelSope.
Hugging Face:https://huggingface.co/collections/Qwen/qwen3-67dd247413f0e2e4f653967f
ModelScope:https://modelscope.cn/collections/Qwen3-9743180bdc6b48
For more usage examples, check out the image below!
https://x.com/Alibaba_Qwen/status/1921907010855125019We’re officially releasing the quantized models of Qwen3 today! Now you can deploy Qwen3 via Ollama, LM Studio, SGLang, and vLLM — choose from multiple formats including GGUF, AWQ, and GPTQ for easy local deployment. Find all models in the Qwen3 collection on Hugging Face and ModelSope. Hugging Face:https://huggingface.co/collections/Qwen/qwen3-67dd247413f0e2e4f653967f ModelScope:https://modelscope.cn/collections/Qwen3-9743180bdc6b48 📷 For more usage examples, check out the image below! https://x.com/Alibaba_Qwen/status/19219070108551250190 Comments ·0 Shares ·2K Views ·0 Reviews -
Google recently announced the early access release of Gemini 2.5 Pro Preview (I/O edition), an updated version of their AI model designed to enhance coding capabilities. This new version focuses on building interactive web apps and improving tasks like code transformation, editing, and creating complex workflows. Originally planned for release at Google I/O, they decided to share it earlier due to high demand and excitement around its potential. If you're into coding or developing smart applications, this tool seems promising for simplifying and enhancing your work. https://youtu.be/6lNuSuyv6RQ
For more details, you can check out updates on [Google I/O](https://io.google/).
https://blog.google/products/gemini/gemini-2-5-pro-updates/Google recently announced the early access release of Gemini 2.5 Pro Preview (I/O edition), an updated version of their AI model designed to enhance coding capabilities. This new version focuses on building interactive web apps and improving tasks like code transformation, editing, and creating complex workflows. Originally planned for release at Google I/O, they decided to share it earlier due to high demand and excitement around its potential. If you're into coding or developing smart applications, this tool seems promising for simplifying and enhancing your work. https://youtu.be/6lNuSuyv6RQ For more details, you can check out updates on [Google I/O](https://io.google/). https://blog.google/products/gemini/gemini-2-5-pro-updates/ 0 Comments ·0 Shares ·2K Views ·0 Reviews
0 Comments ·0 Shares ·2K Views ·0 Reviews -
Google has recently unveiled the Gemini 2.5 Pro Preview “I/O Edition,” a cutting-edge AI model with a focus on advanced coding capabilities. Released ahead of the official Google I/O event due to high developer interest, this model aims to assist programmers by improving code generation, debugging, and overall efficiency in development workflows. If you're into coding or software development, this could be a game-changer for streamlining your projects! Stay tuned for more updates from Google I/O.
https://generativeai.pub/google-releases-gemini-2-5-pro-preview-i-o-edition-with-improved-coding-capability-edc70fa03b8cGoogle has recently unveiled the Gemini 2.5 Pro Preview “I/O Edition,” a cutting-edge AI model with a focus on advanced coding capabilities. Released ahead of the official Google I/O event due to high developer interest, this model aims to assist programmers by improving code generation, debugging, and overall efficiency in development workflows. If you're into coding or software development, this could be a game-changer for streamlining your projects! Stay tuned for more updates from Google I/O. https://generativeai.pub/google-releases-gemini-2-5-pro-preview-i-o-edition-with-improved-coding-capability-edc70fa03b8c0 Comments ·0 Shares ·2K Views ·0 Reviews -
If you're part of a product team and looking to innovate efficiently, AI prototyping platforms might be worth exploring. These tools allow you to quickly build prototypes, gather user feedback, and make decisions based on real data. They can help streamline your design process and ensure you're creating features that truly resonate with users. It's all about smarter, faster development with user-centric insights. Check out more about these platforms here: https://www.magicpatterns.com/If you're part of a product team and looking to innovate efficiently, AI prototyping platforms might be worth exploring. These tools allow you to quickly build prototypes, gather user feedback, and make decisions based on real data. They can help streamline your design process and ensure you're creating features that truly resonate with users. It's all about smarter, faster development with user-centric insights. Check out more about these platforms here: https://www.magicpatterns.com/0 Comments ·0 Shares ·2K Views ·0 Reviews
-
Ever wondered what it would be like to have your very own computer assistant? Look no further! Dive into the future of AI with this incredible tool that makes complex tasks a breeze. Whether you're curious about AI or just want to explore something cool, this is the perfect place to start!
Check it out here https://huggingface.co/spaces/smolagents/computer-agent
Let this smart agent simplify your life and show you the power of cutting-edge technology in action. Trust me, you don’t want to miss this!
#AI #TechInnovation #FutureIsNow #ArtificialIntelligence #CoolTech #DigitalAssistant #SmarterLiving #TechTrends #AIForEveryone #NextGenTech #ExploreAI #TechLife #Innovation #AICommunity #TechMagic🚀 Ever wondered what it would be like to have your very own computer assistant? 🤖 Look no further! Dive into the future of AI with this incredible tool that makes complex tasks a breeze. Whether you're curious about AI or just want to explore something cool, this is the perfect place to start! 🌟 Check it out here 👉 https://huggingface.co/spaces/smolagents/computer-agent Let this smart agent simplify your life and show you the power of cutting-edge technology in action. Trust me, you don’t want to miss this! 💻✨ #AI #TechInnovation #FutureIsNow #ArtificialIntelligence #CoolTech #DigitalAssistant #SmarterLiving #TechTrends #AIForEveryone #NextGenTech #ExploreAI #TechLife #Innovation #AICommunity #TechMagic0 Comments ·0 Shares ·3K Views ·0 Reviews -
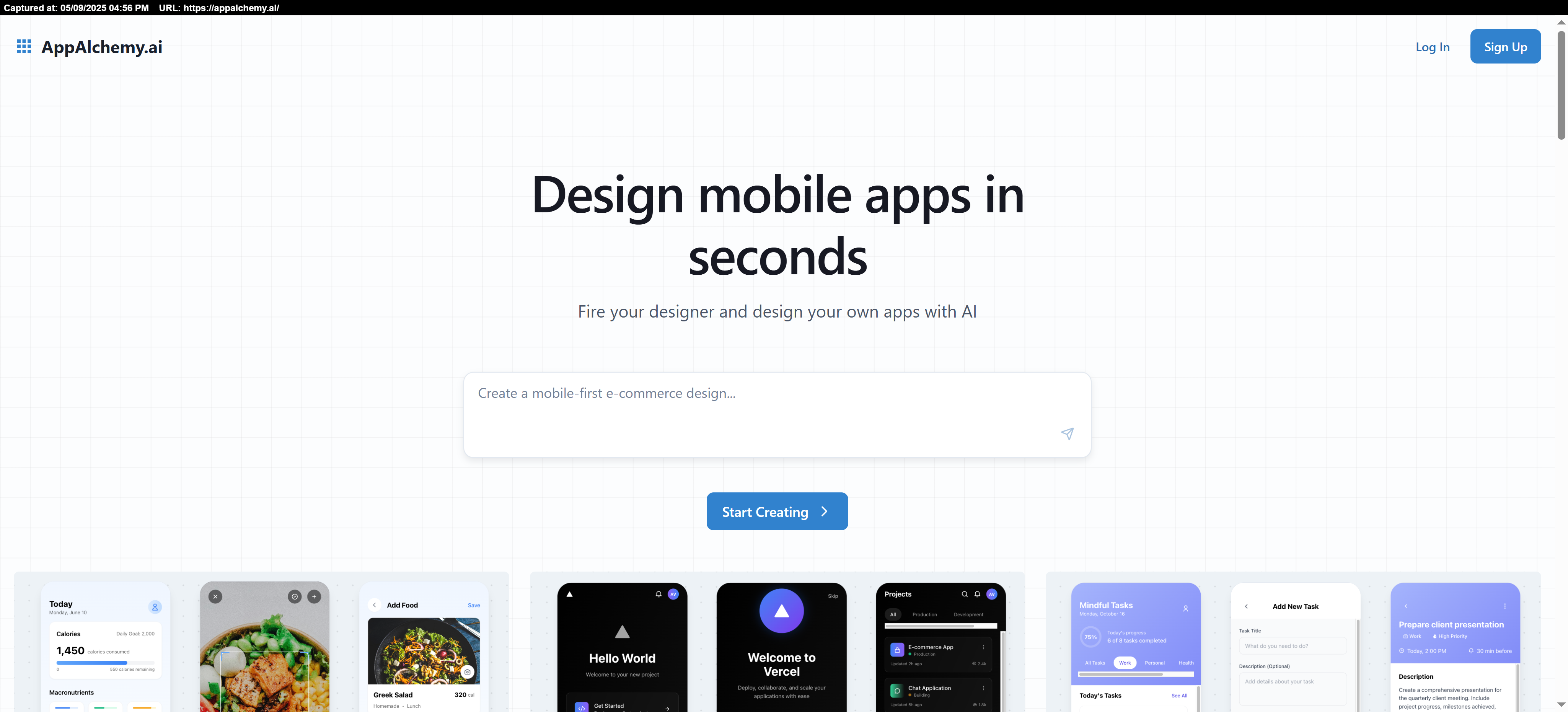
Ready to bring your ideas to life like never before? Dive into the world of creativity and innovation with App Alchemy! Whether you're a dreamer, creator, or entrepreneur, this platform is your ultimate tool to turn visions into reality. No technical skills? No problem! App Alchemy makes it simple, fun, and accessible for everyone.
Start creating today and see the magic unfold! Click here to explore: https://appalchemy.ai/
#Innovation #Creativity #AppAlchemy #NoCode #TechMadeSimple #DreamBig #EntrepreneurLife #DigitalTransformation #FutureOfTech #StartUpJourney #TechForAll #CreateYourOwn #BuildYourDreams #SimpleTech #ExplorePossibilities🚀 Ready to bring your ideas to life like never before? 🌟 Dive into the world of creativity and innovation with App Alchemy! Whether you're a dreamer, creator, or entrepreneur, this platform is your ultimate tool to turn visions into reality. No technical skills? No problem! App Alchemy makes it simple, fun, and accessible for everyone. ✨ Start creating today and see the magic unfold! Click here to explore: https://appalchemy.ai/ #Innovation #Creativity #AppAlchemy #NoCode #TechMadeSimple #DreamBig #EntrepreneurLife #DigitalTransformation #FutureOfTech #StartUpJourney #TechForAll #CreateYourOwn #BuildYourDreams #SimpleTech #ExplorePossibilities0 Comments ·0 Shares ·3K Views ·0 Reviews -
OpenAI has recently shared insights into how they are evolving their organizational structure to better foster innovation and ensure safety in AI development. This move is aimed at enhancing collaboration, transparency, and efficiency as they continue to push the boundaries of artificial intelligence. By refining their structure, OpenAI is working to address the challenges of scaling AI responsibly while delivering impactful solutions for the future. Som say its OpenAI backtracking from seeking to be a "For-Profit" company .. whats your take on this ?
Learn more about their approach here: https://openai.com/index/evolving-our-structure
Explore more about OpenAI: https://openai.com
#OpenAI #ArtificialIntelligence #AIInnovation #TechDevelopment #AIResearch #ResponsibleAI #FutureOfAI #MachineLearning #AICommunity #AIProgress/OpenAI has recently shared insights into how they are evolving their organizational structure to better foster innovation and ensure safety in AI development. This move is aimed at enhancing collaboration, transparency, and efficiency as they continue to push the boundaries of artificial intelligence. By refining their structure, OpenAI is working to address the challenges of scaling AI responsibly while delivering impactful solutions for the future. Som say its OpenAI backtracking from seeking to be a "For-Profit" company .. whats your take on this ? Learn more about their approach here: https://openai.com/index/evolving-our-structure Explore more about OpenAI: https://openai.com #OpenAI #ArtificialIntelligence #AIInnovation #TechDevelopment #AIResearch #ResponsibleAI #FutureOfAI #MachineLearning #AICommunity #AIProgress/0 Comments ·0 Shares ·3K Views ·0 Reviews -
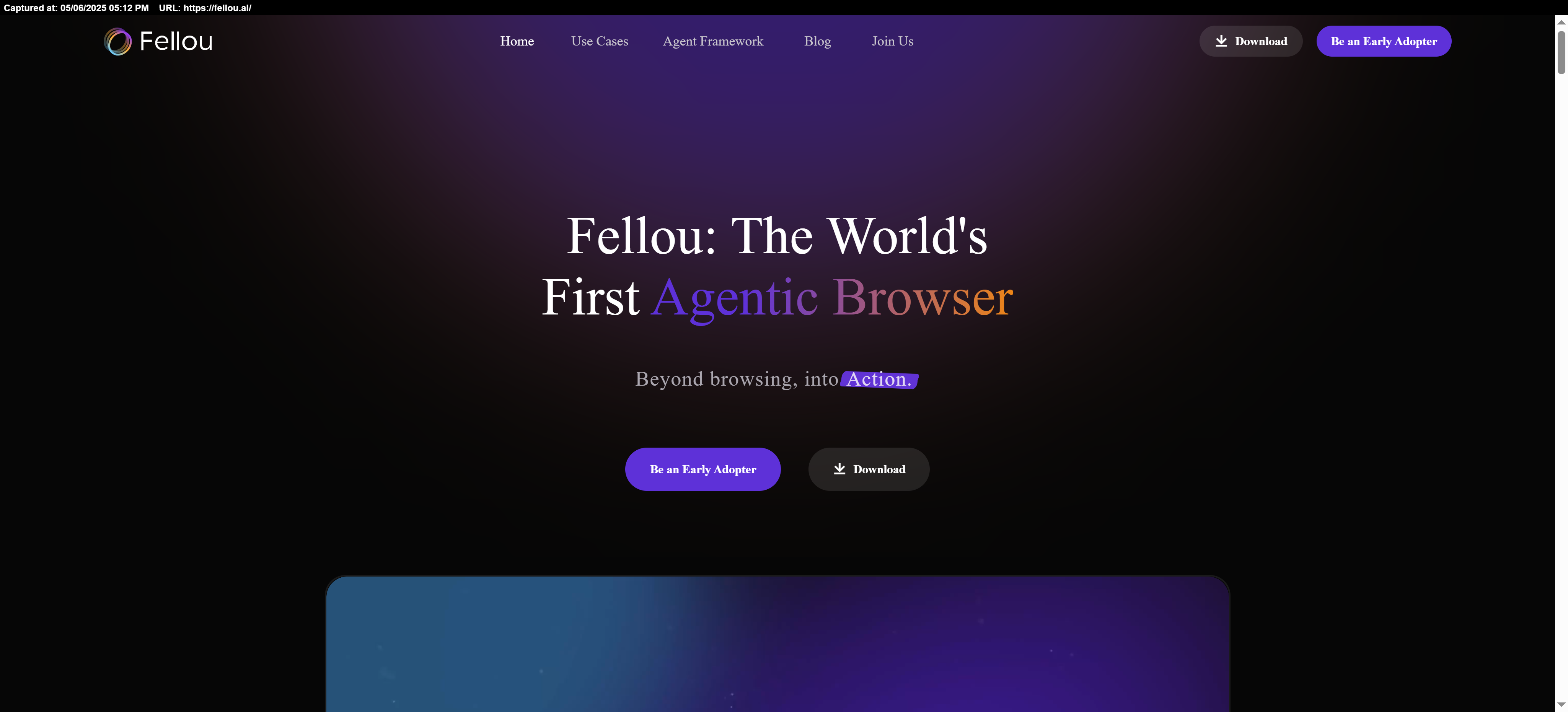
Have you heard of agentic browsers? Fellou is a fascinating example of this innovation. It’s designed to handle complex tasks automatically using something called Deep Action technology. Essentially, it can perform hands-free research and automate workflows across different platforms, saving you time and effort. For those who juggle multiple online tasks, this could be a game-changer! You can learn more about it here: [Fellou](https://fellou.com).
Check it out here: https://fellou.ai/
#AI #ArtificialIntelligence #TechInnovation #FutureOfWork #DigitalTransformation #SmartSolutions #AIForEveryone #NextGenTech #Innovation #Entrepreneurship #TechTools #AIPlatform #Automation #TechLovers #FellouAIHave you heard of agentic browsers? Fellou is a fascinating example of this innovation. It’s designed to handle complex tasks automatically using something called Deep Action technology. Essentially, it can perform hands-free research and automate workflows across different platforms, saving you time and effort. For those who juggle multiple online tasks, this could be a game-changer! You can learn more about it here: [Fellou](https://fellou.com). 👉 Check it out here: https://fellou.ai/ #AI #ArtificialIntelligence #TechInnovation #FutureOfWork #DigitalTransformation #SmartSolutions #AIForEveryone #NextGenTech #Innovation #Entrepreneurship #TechTools #AIPlatform #Automation #TechLovers #FellouAI0 Comments ·0 Shares ·3K Views ·0 Reviews -
Exciting Opportunity Alert! Are you passionate about AI and eager to make a real impact? Pareto is looking for talented individuals to join their team as AI Trainers! This is your chance to be part of an innovative company shaping the future of artificial intelligence. Whether you're a curious learner or a seasoned pro, this role offers an incredible opportunity to grow and thrive.
Don't miss out—apply today and take the first step toward an exciting career in AI! https://pareto.ai/careers/ai-trainer
#AITechnology #AITrainer #CareerOpportunity #FutureOfWork #InnovativeCareers #TechCareers #ArtificialIntelligence #JoinOurTeam #WorkWithUs #AIJobs #TechInnovation #JobSearch #CareerGoals #WeAreHiring #TechCommunity🚀 Exciting Opportunity Alert! 🌟 Are you passionate about AI and eager to make a real impact? Pareto is looking for talented individuals to join their team as AI Trainers! This is your chance to be part of an innovative company shaping the future of artificial intelligence. Whether you're a curious learner or a seasoned pro, this role offers an incredible opportunity to grow and thrive. 🌐✨ Don't miss out—apply today and take the first step toward an exciting career in AI! 👉 https://pareto.ai/careers/ai-trainer #AITechnology #AITrainer #CareerOpportunity #FutureOfWork #InnovativeCareers #TechCareers #ArtificialIntelligence #JoinOurTeam #WorkWithUs #AIJobs #TechInnovation #JobSearch #CareerGoals #WeAreHiring #TechCommunity0 Comments ·0 Shares ·3K Views ·0 Reviews -
Ready to level up your skills and explore new career paths? Whether you're just starting out or looking to expand your knowledge, this incredible resource has everything you need to succeed! From web development to data science, discover step-by-step roadmaps tailored to your goals. Don’t wait—start your journey today and unlock your full potential!
Check it out here: https://roadmap.sh/
#LearnAndGrow #CareerGoals #SkillUp #TechJourney #WebDevelopment #DataScience #SelfImprovement #KnowledgeIsPower #StayCurious #TechLearning #OnlineResources #SkillBuilding #NeverStopLearning #TechSkills #LevelUpYourLife🚀 Ready to level up your skills and explore new career paths? 🌟 Whether you're just starting out or looking to expand your knowledge, this incredible resource has everything you need to succeed! 📚 From web development to data science, discover step-by-step roadmaps tailored to your goals. Don’t wait—start your journey today and unlock your full potential! 💡✨ 👉 Check it out here: https://roadmap.sh/ #LearnAndGrow #CareerGoals #SkillUp #TechJourney #WebDevelopment #DataScience #SelfImprovement #KnowledgeIsPower #StayCurious #TechLearning #OnlineResources #SkillBuilding #NeverStopLearning #TechSkills #LevelUpYourLife0 Comments ·0 Shares ·3K Views ·0 Reviews -
Discover the Future of AI Assistance!
Hey everyone! Have you ever wondered how AI can make your life easier and more productive? Check out RA-Aid, the ultimate AI tool designed to transform how you work, learn, and create. Whether you're a student, professional, or just curious about technology, RA-Aid has something amazing for you!
Dive into the world of AI now: https://www.ra-aid.ai/
Let RA-Aid be your guide to smarter solutions and endless possibilities. Don't miss out on the AI revolution!
#AIRevolution #TechInnovation #SmartSolutions #FutureTech #DigitalTransformation #AIforEveryone #ExploreAI #InnovationUnleashed #TechSavvy #AICommunity #NextGenTech #AIInspiration #ProductivityBoost #LearnWithAI #DiscoverTheFuture🚀 Discover the Future of AI Assistance! 🌟 Hey everyone! Have you ever wondered how AI can make your life easier and more productive? 🤔 Check out RA-Aid, the ultimate AI tool designed to transform how you work, learn, and create. Whether you're a student, professional, or just curious about technology, RA-Aid has something amazing for you! 💡 👉 Dive into the world of AI now: https://www.ra-aid.ai/ ✨ Let RA-Aid be your guide to smarter solutions and endless possibilities. Don't miss out on the AI revolution! 🔥 #AIRevolution #TechInnovation #SmartSolutions #FutureTech #DigitalTransformation #AIforEveryone #ExploreAI #InnovationUnleashed #TechSavvy #AICommunity #NextGenTech #AIInspiration #ProductivityBoost #LearnWithAI #DiscoverTheFuture0 Comments ·0 Shares ·3K Views ·0 Reviews
More Stories